本文摘抄自《Java 多线程编程实战指南》核心篇 第五章小结
本章介绍了多线程编程中线程间常见的协作形式以及 Java 平台对这些协作形式所提出的支持。
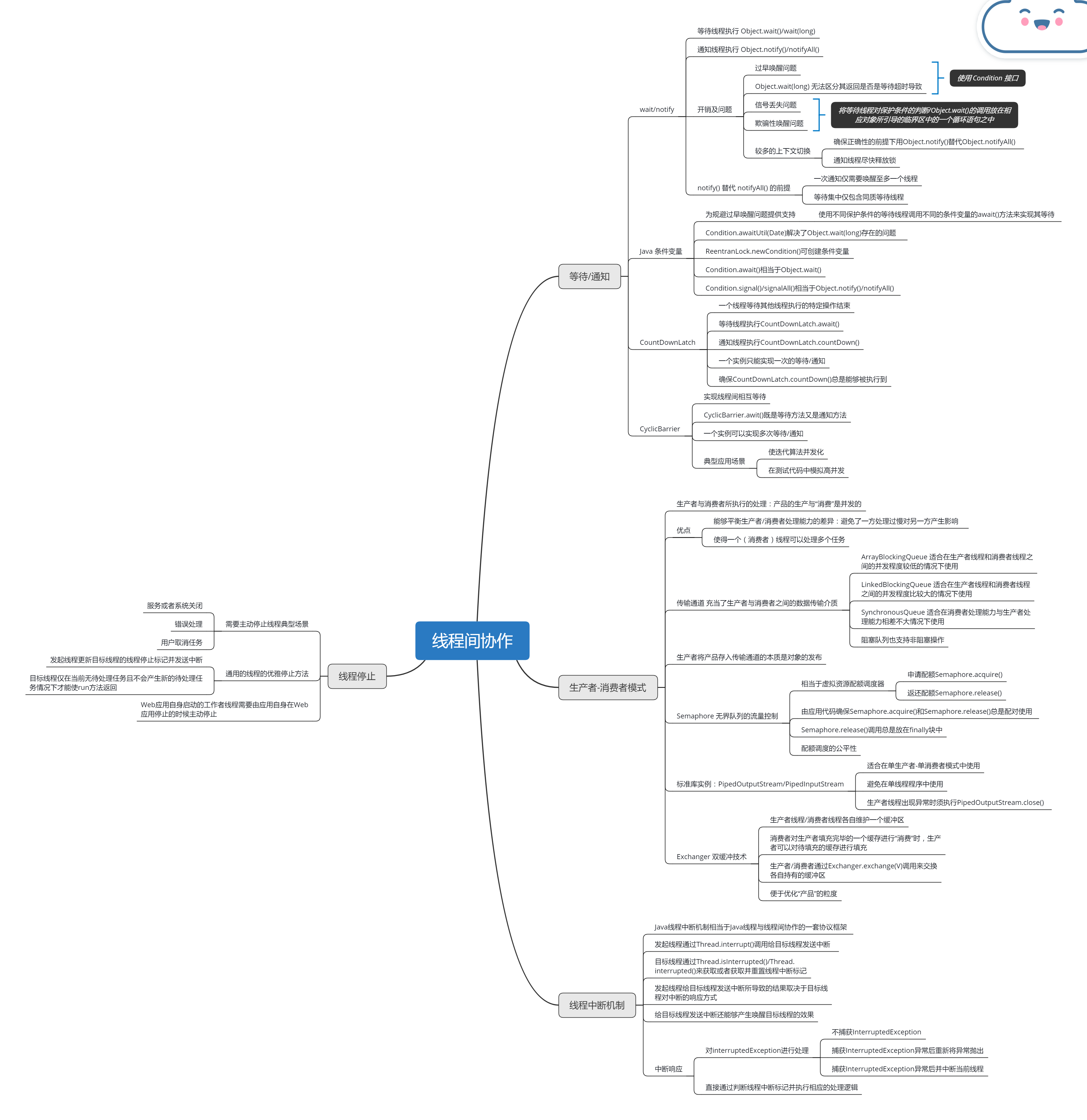
等待线程可以通过执行 Object.wait()/wait(long) 来实现等待。通知线程可以通过执行 Object.notify()/notifyAll() 来实现通知。等待线程/通知线程在执行 Object.wait()/wait(long)/Object.notify()/notifyAll() 时必须持有相应对象对应的内部锁。为了避免信号丢失问题以及欺骗性唤醒问题,等待线程将等待线程对保护条件的判断/Object.wait()/wait(long) 的调用必须放在相应对象所引导的临界区中的一个循环语句之中。
使用 notify() 替代 notifyAll() 必须使以下两个条件同时得以满足:
- 一次通知仅需要唤醒至多一个线程;
- 相应对象上的所有等待线程都是同质等待线程。
使用 notify() 替代 notifyAll() 可以减少等待/通知中产生的上下文切换。通知线程在执行完 Object.notify()/notifyAll() 后尽快释放相应对象的内部锁也有助于减少上下文切换。
条件变量(Condition 接口)是 wait/notify 的替代品。Condition 接口的 API 与 wait/notify 类似:Condition.await()/awaitUtil(Date) 相当于 Object.wait()/wait(long);Condition.signal()/signalAll() 相当于 Object.notify()/notifyAll()。Condition.awaitUtil(Date) 解决了 Object.wait(long) 存在的问题——无法区分其返回是否是由等待超时而导致的。
Condition 接口本身只是对解决过早唤醒问题提供了支持。要真正解决过早唤醒问题,我们需要通过应用代码维护保护条件与条件变量之间的对应关系,即使用不同保护条件的等待线程需要调用不同的条件变量的 await 方法来实现其等待,并使通知线程在更新了相关共享变量之后,仅调用与这些共享变量有关的保护条件所对应的条件变量的 signal/signalAll 方法来实现通知。
CountDownLatch 能够用来实现一个线程等待其他线程执行的特定操作的结束。等待线程执行 CountDownLatch.await(),通知线程执行 CountDownLatch.countDown()。为避免等待线程永远处于暂停状态而无法被唤醒,CountDownLatch.countDown() 调用通常需要被放在 finally 块中。一个 CountDownLatch 实例只能实现一次等待/通知。对于同一个 CountDownLatch 实例 latch,latch.countDown() 的执行线程在执行该方法之前所执行的任何内存操作,对等待线程在 latch.await() 调用返回之后的代码是可见的且有序。
CyclicBarrier 能够用于实现多个线程间的相互等待。CyclicBarrier.await() 既是等待方法又是通知方法。CyclicBarrier 实例的所有参与方除最后一个线程外都相当于等待线程,最后一个线程则相当于通知线程。与 CountDownLatch 不同的是,CyclicBarrier 实例是可以复用的——一个 CyclicBarrier 实例可以实现多次等待/通知。在使用 CountDownLatch 足以满足要求的情况下,我们应该避免使用 CyclicBarrier。CyclicBarrier 的典型应用场景包括:使迭代(Iterative)算法并发化,在测试代码中模拟高并发。
在生产者——消费者模式中,生产者负责生产产品并通过传输通道将产品以线程安全的方式发布到消费者线程。消费者线程仅负责从传输通道中取出产品进行“消费”。产品既可以是数据,也可以是待处理的任务。BlockingQueue 的实现类 ArrayBlockingQueue/LinkedBlockingQueue 和 SynchronousQueue 等以及 Exchanger 类可作为传输通道。
生产者与消费者所执行的处理,即产品的生产与“消费”是并发的。这使得我们能够平衡生产者/消费者处理能力的差异,即避免了一方处理过慢对另一方产生影响。另外,生产者——消费者模式使得一个线程(消费者线程)可以处理多个任务,提高了线程的利用率。
使用无界队列作为传输通道时往往需要借助 Semaphore 控制生产者的生产速率。Semaphore 相当于能够对程序访问虚拟资源的并发程度进行控制的配额调度器。Semaphore.acquire() 用于申请配额,Semaphore.release() 用于返还配额,Semaphore.release() 调用总是放在 finally 块中。Semaphore.acquire() 和 Semaphore.release() 总是配对使用的,这点需要由应用代码来确保。Semaphore 对配额的调度既支持非公平策略(默认策略),也支持公平策略。
PipedOutputStream/PipedInputStream 是 Java 标准库类中生产者——消费者模式的一个具体例子。PipedOutputStream/PipedInputStream 适合在单生产者——单消费者模式中使用,应避免在单线程程序中使用 PipedOutputStream/PipedInputStream。生产者线程发生异常而导致其无法继续提供新的数据时,生产者线程必须主动提前关闭相应的 PipedOutputStream 实例(调用 PipedOutputStream.close())。
Exchanger 类也可作为传输通道,它对双缓冲技术提供了支持:生产者与消费者各自维护一个缓冲区,双方通过执行 Exchanger.exchange(V) 来交换各自持有的缓冲区。当消费者在“消费”一个已填充完毕的缓冲区时,生产者可以对待填充的缓冲区进行填充(生产产品),从而实现了产品的“消费”与生成的并发。Exchanger 类便于我们能够对产品的粒度进行优化。
Java 线程中断机制相当于 Java 线程与线程间协作的一套协议框架:发起线程通过 Thread.interrupt() 调用给目标线程发送中断,这相当于将目标线程的线程中断标记置为 true;目标线程则通过 Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()/Thread.interrupted() 来获取或者获取并重置线程中断的响应方式。给目标线程发送中断还能够产生唤醒目标线程的效果。目标线程可以通过对 InterruptedException 进行处理的方式或者直接通过判断线程中断标记并执行相应的处理逻辑的方式来响应中断。对 InterruptedException 进行处理的正确方式包括:不捕获InterruptedException/捕获 InterruptedException 后重新将该异常抛出,以及捕获 InterruptedException 并在捕获该异常后中断当前线程。
需要主动停止线程的典型场景包括:服务或者系统关闭/错误处理以及用户取消任务。通用的线程优雅停止办法:发起线程更新目标线程的线程停止标记并给其发送中断,目标线程仅在当前无待处理任务且不会产生新的待处理任务情况下才能使 run 方法返回。Web 应用自身启动的工作者线程需要由应用自身在 Web 应用停止时主动停止。